Introduction Understanding Excel's AutoSave Feature
Excel's AutoSave feature is designed to protect your work by automatically saving your files, minimizing the risk of data loss due to crashes, power outages, or accidental closures. Available in modern versions of Microsoft Office, it saves your files in the cloud, making it easier to recover previous versions.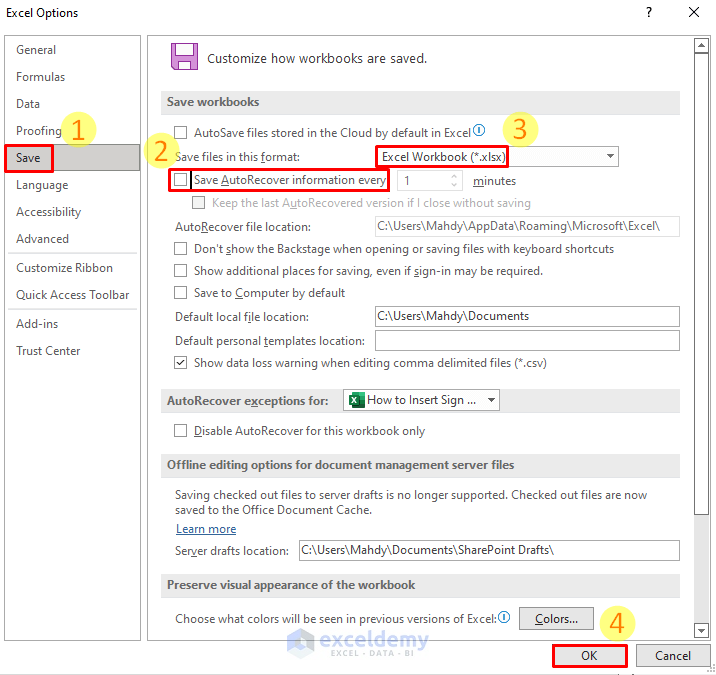
This guide will walk you through how to enable, disable, and understand the nuances of AutoSave, ensuring you're equipped to safeguard your important Excel spreadsheets.
Enabling How to Enable AutoSave in Excel
AutoSave is typically enabled by default when you save your Excel file to OneDrive, SharePoint, or Teams. If you see the AutoSave toggle in the top left corner of your Excel window (near the Quick Access Toolbar), it's already active. Clicking it will toggle between on and off.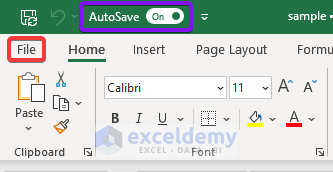
Ensure you are signed in to your Microsoft account within Excel to take full advantage of the feature.
Disabling Turning Off AutoSave
To disable AutoSave, click the AutoSave toggle in the upper-left corner of the Excel window. This will prevent automatic cloud saves. Alternatively, you can adjust the AutoRecover settings to control how often Excel automatically saves backup copies for local recovery (this is different from AutoSave).
To change AutoRecover settings, go to File > Options > Save and adjust the 'Save AutoRecover information every' interval. However, disabling AutoSave entirely isn't recommended for data protection.
“AutoSave is your safety net for Excel files. Enable it and rest easy knowing your data is protected.
Excel Expert
Interactive Tools
Explore these useful resources
AutoSave Quick Guide
A concise, step-by-step guide on enabling and disabling AutoSave.
AutoRecover Understanding vs. AutoSave
It's important to differentiate between AutoSave and AutoRecover. AutoSave saves your file in the cloud, while AutoRecover creates temporary backup files stored locally. AutoRecover helps you recover your work if Excel crashes or closes unexpectedly. You can find AutoRecover files by going to File > Info > Manage Workbook > Recover Unsaved Workbooks.
Both features contribute to data protection, but AutoSave offers the added benefit of version history and cloud accessibility.
Troubleshooting Addressing Common AutoSave Issues
If AutoSave isn't working, ensure you're signed in to your Microsoft account and that your file is saved to a cloud location (OneDrive, SharePoint, or Teams). Check your internet connection, as AutoSave requires an active connection to save your work.
Also, verify that you have sufficient storage space in your cloud account. Reviewing your AutoRecover settings periodically can prevent unexpected data loss.