Understanding Foldback Current Limiting
Foldback current limiting is a sophisticated technique employed to safeguard power supply circuits, particularly when dealing with short-circuit conditions. Unlike constant current limiting, which can lead to excessive power dissipation, foldback limiting offers a more efficient approach.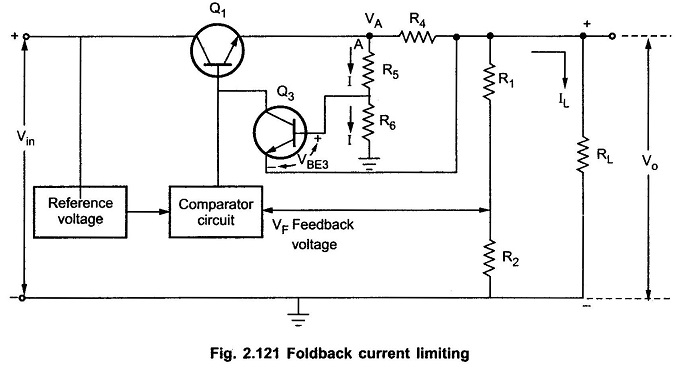
The core advantage of foldback limiting lies in its ability to reduce the short-circuit current, thereby minimizing the stress on the series pass transistor. This allows for the use of smaller, more efficient transistors, ultimately improving the overall design.
Circuit Operation and Design
The foldback circuit modifies the current limit as the output voltage decreases. As the output voltage drops due to a short circuit, the current limit is reduced significantly. This characteristic protects the pass transistor from excessive power dissipation.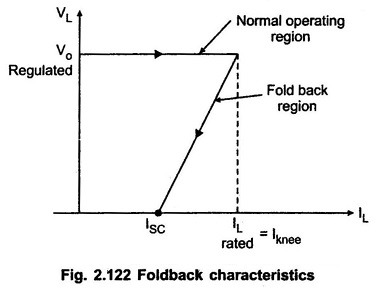
Key components within the circuit, such as resistors and transistors, work together to monitor the output voltage and current. The ratio of the rated load current to the short circuit current is adjustable, giving designers control over the circuit’s protective characteristics.
“Foldback current limiting provides an efficient and reliable method for protecting power supply circuits, enhancing performance and reducing component stress.
Engineering Insight
Explore Further
Dive deeper into circuit design
Circuit Simulation
Interactive simulation to visualize foldback current limiting behavior under various load conditions.
Design Calculator
Calculate component values for optimal foldback characteristics.
Benefits Advantages of Foldback Current Limiting
The primary benefit is the reduction of power dissipation in the series pass transistor during short-circuit events. This enables the utilization of lower power rated transistors.
Foldback limiting improves the efficiency of power supply designs compared to constant current limiting, especially during over-current or short circuit scenarios. The foldback characteristic provides superior protection.