What are Current Limiting Reactors?
Current limiting reactors are inductive coils with high inductive reactance designed to limit short circuit currents during fault conditions. They play a critical role in protecting electrical equipment and ensuring the reliability of power systems.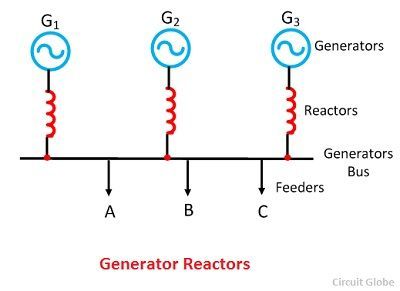
These reactors also reduce voltage disturbances, improving overall system stability. They are strategically installed in various locations, including feeder lines, generator leads, and bus sections, to mitigate the impact of short circuits.
Key Functions of a Current Limiting Reactor
The primary function of a current limiting reactor is to limit the magnitude of short-circuit currents. This is achieved by its high inductive reactance, which restricts the flow of fault current.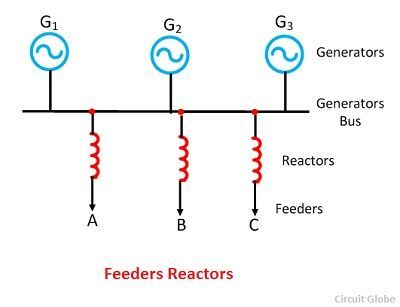
By limiting fault currents, reactors protect electrical appliances from mechanical stress and overheating. They also minimize voltage disturbances caused by short circuits, thereby increasing the chances of continuity of supply.
Reactors allow for the normal interchange of power under standard conditions. When a fault occurs, the disturbance is localized to the faulty section due to the reactor's current-limiting capability.
Reactor Types and Locations of Current Limiting s
Current limiting reactors are installed at various locations within a power system to provide protection. Common locations include generator leads, feeder lines, and bus bars.
Generator reactors are inserted between the generator and the generator bus, protecting individual machines. Feeder reactors are connected in series with feeder lines, localizing faults and preventing their spread. Bus-bar reactors can be used in ring systems and tie-bus systems to limit fault currents and minimize the impact of disturbances.
Generator Reactors
Generator reactors are installed between the generator and the generator bus. Their primary function is to protect individual generators from the impact of short-circuit faults. Typically, the reactor's magnitude is approximately 0.05 per unit.
One potential drawback is that if a fault occurs on one feeder, the entire system can be affected. However, they are still vital for equipment protection.
“Current limiting reactors are the silent guardians of our power grid, protecting critical infrastructure from the devastating effects of short circuits.
Power System Expert
Explore Further
Dive deeper into the world of current limiting reactors
Reactor Animation
Interactive animation showing how a current limiting reactor functions to limit fault current.
Types Quiz
Test your knowledge of different reactor types and their applications.
Cost and Benefits Calculator
Compare the cost and benefits of using current limiting reactors
Feeder Reactors
Feeder reactors are installed in series with the feeder lines. They isolate faults, so when a fault occurs on any one feeder, the voltage drop only occurs in that feeder's reactor, while the bus bar is not affected much.
An advantage is that faults on one feeder do not affect others, localizing the fault's impact. However, they do not provide protection to the generators against short-circuit faults that occur across the bus bars. Also, there is a constant voltage drop and constant power loss in reactors during normal operating conditions.
Bus-Bar Reactors
Bus-bar reactors are inserted into the bus bar, reducing the constant voltage drop and power loss issues. They are commonly used in ring and tie-bus systems.
In ring systems, these reactors connect separate bus sections, enabling one generator to feed the fault while limiting the current from others. This minimizes voltage disturbances to the faulty section only.
The tie-bus system is a modification of the ring system that offers additional advantages. It ensures that fault current doesn't exceed a predefined value, determined by the size of individual reactors.
Potential Drawbacks of Current Limiting Reactors
One of the main drawbacks is the increase in total percentage reactance of the circuit when reactors are installed, potentially reducing the power factor and increasing voltage drop.
This can negatively impact system regulation.