Introduction Understanding the CSS Overflow Property
The CSS overflow property is a crucial tool for controlling how content behaves when it exceeds the boundaries of its container. This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to mastering the overflow property and its different values, including visible, hidden, scroll, and auto. By understanding these values, you can create more dynamic and user-friendly web designs.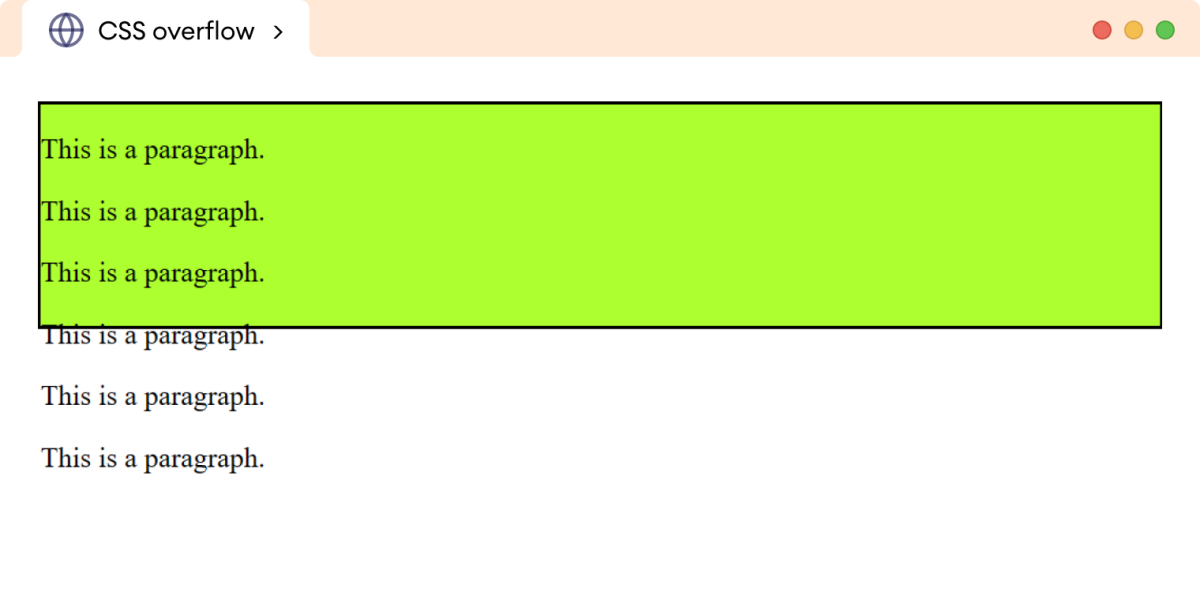
The overflow property is essential for managing content that might be larger than the space allocated for it, ensuring a clean and controlled display. We'll explore each value, providing clear explanations and practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Syntax CSS Overflow
The syntax for the overflow property is straightforward. It is applied to an HTML element and accepts one of several predefined values.
Here's the basic syntax:
`css
element {
overflow: value;
}
`
Where value can be one of the following: visible, hidden, scroll, auto, initial, or inherit.
visible CSS Overflow:
The visible value is the default behavior of the overflow property. With overflow: visible;, content that overflows the element's box is not clipped; it's displayed outside the element's boundaries.
Example:
`html
`In this case, the text will extend beyond the 200x100px container.
hidden CSS Overflow:
The hidden value clips the overflowing content. Any content that exceeds the element's dimensions is hidden, making the element appear clean.
Example:
`html
`The overflowing text will be clipped, and you'll only see the portion of the text that fits within the 200x100px container.
“Understanding the overflow property is crucial for effective web design. It directly impacts how content is displayed and how users interact with your web pages.
Programiz
Interactive Examples
Experiment with the different overflow values:
Live Code Editor
Try out the overflow values with our interactive code editor.
scroll CSS Overflow:
The scroll value adds scrollbars to the element, regardless of whether the content overflows. This allows users to scroll through the content if it exceeds the element's dimensions.
Example:
`html
`Scrollbars will appear, enabling users to scroll both horizontally and vertically if the content overflows in either direction.
auto CSS Overflow:
The auto value adds scrollbars only when the content overflows. This provides a dynamic approach, showing scrollbars only when necessary.
Example:
`html
`Scrollbars will only appear if the content overflows the container. If the content fits, there are no scrollbars.
x and y CSS Overflow-x and Overflow-y Property
The overflow-x property controls horizontal overflow, while overflow-y controls vertical overflow. This gives you more fine-grained control.
Example:
`html
`This example will add a horizontal scrollbar and hide any vertical overflow.